Technical FAQs for "ImageGear"

Today’s customers expect more of software applications than ever before. Piecemeal solutions that provide only a few noteworthy features are quickly being overtaken by more comprehensive platforms that deliver an end-to-end experience for users. This has prompted developers to incorporate more capabilities, while also building innovative features that set their solutions apart from the competition. Thanks to third-party software integrations, they’re able to meet both demands.
What is Third-Party Software Integration?
Third-party software integrations typically come in the form of SDKs or APIs that provide applications with specialized capabilities. Rather than building complex features like optical character recognition (OCR), PDF features, or image cleanup from scratch, developers can instead incorporate the necessary features directly into their software via an SDK or use an API call to access capabilities without expanding their application’s footprint.
From a user experience standpoint, third-party software integrations allow developers to build more cohesive software solutions that provide all the essential features a customer may require. Instead of pushing them into a separate application to interact with documents, provide a signature, or fill out a digital form, they can instead deliver an unbroken experience that’s easier to navigate and manage from start to finish.
4 Key Third-Party Software Benefits
There are a number of important benefits organizations can gain from using third-party software integrations, but four stand out in particular:
1. Reduce Development Costs
When evaluating whether it makes sense to build functionality for an application in-house or buy a third-party software integration, cost is frequently one of the key considerations. There is often a tendency to think that it would be more cost-effective to have developers already working on the project simply build the capabilities they need on their own. After all, there’s no shortage of open-source SDKs and other tools that are available without having to pay licensing or product fees.
In practice, however, this approach usually ends up being more expensive in the long run. That’s because the developers working on the project often lack the experience needed to build those capabilities quickly. A software engineer hired to help build AI software, for instance, probably doesn’t know a lot about file conversion or annotation. While they might be able to find an open-source tool to build those features, they still need to do quite a bit of development work and on-the-job learning to get the new capabilities stood up and thoroughly tested.
Focusing on these features means they’re not focusing on the more innovative aspects of their application. From a cost standpoint, that means they’re being paid to build something that’s already readily available in the market. When these internal development costs are taken into account, it’s almost always more cost effective to buy ready-to-implement software features built by an experienced third party. As the saying goes, there’s no reason to reinvent the wheel.
2. Get to Market Faster
Software developers are always working against the clock. With new applications hitting the market faster than ever, there’s tremendous pressure to keep development timelines on track and avoid missing important deadlines. This helps projects stay within their expected budgets and prevents potential competitors from getting to market faster. Any steps that can be taken to accelerate development and potentially shorten the timeline to releasing a product could mean the difference between becoming an industry innovator or being labeled as an also-ran.
Third-party software integrations allow developers to quickly and seamlessly integrate essential capabilities into applications without compromising their project timeline. Rather than building features like forms processing, document annotation, and image conversion from scratch, teams can instead use third-party SDKs and APIs to add proven, reliable, and secure features in a fraction of the time. By keeping projects on or ahead of schedule, they can focus on delivering a better, more robust product that exceeds customer expectations.
3. Expand Application Features & Functionality
Software development teams typically possess the experience and expertise needed to build the core architecture and innovative features of a new application. In many cases, they’re designing something novel that will provide a point of differentiation in the market. The more time they can spend on refining and expanding those capabilities, the more likely the application is to make an impact and win over customers.
What these developers often lack, however, are the skills needed to implement a variety of other features that will enhance the application’s functionality. Features like document conversion, OCR, PDF support, digital forms, eSignature, and image compression are complex and difficult to build from scratch. By integrating third-party software, developers can leverage proven, feature-rich technology to expand their application’s capabilities. This not only allows them to improve their solution’s versatility but also enhance the overall user experience by eliminating the need for external programs or troublesome plug-ins.
4. Access Specialized Engineering Support
Incorporating features like PDF support, image conversion, and document redaction into an application poses several challenges. Some of those challenges don’t show up right away, instead, they become evident long after a software product launches. If the developers don’t have a lot of experience with the technology behind those features, minor issues can quickly escalate into serious problems that leave customers unhappy and willing to look elsewhere for alternatives. No organization wants to be caught in a situation where a bug embedded in an open-source tool renders a client’s valuable assets unusable.
By leveraging proven, tested, and secure third-party software integrations, developers gain access to support from experienced engineering teams with deep knowledge of their solutions. In addition to documentation and code samples, they can also speak directly with developers who can provide guidance on how to best integrate features and resolve issues when they emerge. The best integration providers will even work with organizations to customize their solutions to meet specific application needs, which helps create even smoother user experiences and enhances reliability.
Integrating Third-Party Software with Accusoft
For over 30 years, Accusoft has helped organizations add essential features like barcode recognition, file conversion, document assembly, and image compression to their applications through an innovative line of SDKs and APIs. Our document lifecycle technologies are backed by multiple patents and have been incorporated successfully into a wide range of applications. Our dedicated engineers provide ongoing support and work closely with customers to implement their specific use cases, ensuring that their software platform is delivering the best possible experience.
To learn more about integrating third-party software with Accusoft SDKs and APIs, talk to one of our solutions experts today.

These days there is a heightened awareness of the risk of opportunity for a data breach or cyber attack. Whether the spike in attention came from a global pandemic, brink of international war, or an unknown hacker that set its sights on Elon Musk, there is a general consensus that our personal data is at risk at any point through a breach of security. This becomes more potent for companies as the cost of such insecurity could potentially end its tenure. According to an IBM Data Breach Report, 2021 had the highest average data breach cost in a 17-year history of $4.24M. Securing data and maintaining an individual’s privacy is a priority for many organizations throughout the world, but following a strict standard has only been attempted by the European Union (EU) thus far.
The EU has taken this priority a step further than just suggesting companies and organizations increase data protection – since 2018, they’ve mandated and enforced specific requirements through the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Given the broad parameters covered under GDPR compliance, ensuring the standards are met can become a time-consuming, stressful and ongoing issue if not resourced properly. The parameters go beyond the protection of personal data and go as far as requirements, to prove security measures are set in place.
Who Needs to Maintain GDPR Compliance?
While often only associated within the European Union, the requirements and legislation of the GDPR extend as far as all “entities who are offering goods or services to anyone residing in the EU (even if those services are provided free of cost). Any global business either has to become compliant for all of its users/customers or be able to accurately identify EU residents and enable compliant systems to handle only that subset of the customer base.”
GDPR requires companies to know the following as related to personal data:
- What personal data is being shared
- Where it is being shared
- How it can be deleted at a moment’s notice if necessary
The GDPR also highly encourages that an organization designates an employee to be the point of contact and in control of the data security processes and systems to maintain compliance. A first step to having an effective process in place is choosing the right tools with security features to protect data being shared within the company.
Managing Risk through Secure Document Viewing
As risk management becomes an essential part of strategic planning, the importance of IT security and data encryption skyrockets to the top of priorities for most companies. GDPR suggests encryption as a means to manage risk in file sharing but does not outline explicit instruction. With PrizmDoc™ Viewer, companies gain added data security, aligned with GDPR compliance, in document viewing and sharing without heavy client-side installations or downloads.
PrizmDoc™ Viewer is created with Multi-Level Data Protection including:
- 256-bit AES encryption
- (Advanced Encryption Standard) is an international standard that ensures data is encrypted/decrypted following this approved standard. It ensures high security and is adopted by the U.S. government and other intelligence organizations across the world.
- Configurable user permissions add a strong measure of privacy and protection to document content.
A Simple Path to Secure Document Sharing
Remote work or not – collaborating on a project today means sharing documents among many colleagues to finalize a document, project, or presentation. To do that with security in mind, organizations are cobbling together tech stacks to meet their productivity needs along the way, and several different file types can come across their desks in a single day.
PrizmDoc™ Viewer integrates into your current application to render and display a multitude of file types with high fidelity and speed. The ease of use features include:
- Flexible use across many platforms
- A self-hosted version that resides on any organization’s servers
- Empowers developers to provide their users with responsive file viewing
- Search and redaction can be easily turned on/off
PrizmDoc Viewer is also designed to run on all devices with a zero-footprint viewer that makes it easy for employees to work where and how they wish. The white label services give an organization the flexibility to brand and customize while gaining peace of mind in data security.
Open and View an Image Securely the First Time
While documents have a range of formats from Word, PDF, spreadsheets, and more – images are often more of a culprit when it comes to difficulty viewing, let alone being able to download, edit, markup, or save information as a separate file. Workers find themselves quickly downloading a media player just to open the image. Having multiple solutions in place is not only confusing, but it also contributes to inefficiency and human error which means added risk for images to remain secure.
As photographs can constitute personal data under the GDPR, this means organizations must be able to quickly and easily remove all images where the individual can be identified.
With ImageGear, an organization is able to add powerful image processing capabilities that enhance secure collaboration such as:
- PDF manipulation that includes managing access with digital signatures for added security levels
- The image processing library offers developers a set of methods for modifying an image including to resize, crop, merge, rotate, and flip.
- An option to add OCR for document search and data capture support
Getting Started
To quickly gain peace of mind with secure collaboration, contact us today.

Having the right file conversion tools in place can make or break an application. Developers frequently face the challenge of managing multiple file types within a consolidated workflow. Without effective conversion tools, users are forced to rely on external applications that compromise both efficiency and security.
Out of all the file formats developers must account for, PDFs remain among the most important. The ability to convert a wide variety of document and image file types into PDF format can provide an application with unmatched versatility. In fact, PDF conversion support is one of the keys to unlocking better workflow performance, security, and collaboration.
5 Reasons to Convert Files to PDF
1. PDF Format is Consistent
Sharing documents and images across different devices and operating systems can sometimes create problems if the recipient lacks the up-to-date software necessary to view the file properly. This is a particular challenge with documents created using Microsoft Word since the formatting could look quite different across different versions of the program. Since PDF files are designed to look the same no matter how they’re being viewed, the format is ideal for sharing. Both documents and images can display equally well as PDFs, so converting files into this format is a quick and easy way to make them accessible for viewing.
2. PDF Files Are Easily Compressed
Sharing large image files can be a challenge for many organizations. High-resolution JPEG or TIFF files are often too large to share over email or web-based applications. Converting them to compressed PDFs is a quick way to reduce file size for easier sharing while still retaining a copy of the original file. Since the compressed version is in PDF format, there is less chance of version confusion when someone needs to access the original source image.
3. PDFs Are Widely Supported
Although PDFs once required specialized viewing software, thanks to JavaScript-based libraries like PDF.js, they can now be viewed by a conventional web browser. For all intents and purposes, this has made PDF a universal file format that can be viewed on any device. Converting a file into PDF ensures that it will be accessible to anyone who is granted access to it, regardless of the device or operating system they’re using.
4. PDFs Offer Security Protections
For many organizations, protecting privacy and confidential information is incredibly important. Converting document and image files into PDF format allows them to take advantage of the standard’s security features. Passwords can be set to authorize viewing and editing access to a file, which not only helps to ensure privacy but also limits who can make changes to a file so version control is easier to maintain. Files can also be converted into PDF/A format for secure archival purposes.
5. PDFs Support Annotation Markups
Most PDF viewing solutions support some form of annotation markups, which allows multiple contributors to make notes and comments on a file. Converting documents or images into a PDF facilitates this collaboration while safely preserving the original version of the file for future reference. Since PDF viewers provide a variety of annotation tools, they offer a great deal of flexibility when it comes to marking up images and documents without having to depend upon specialized software. Image and document files with additional annotation layers can also be converted into flattened PDFs for easier viewing.
Converting Files to PDF Using ImageGear
Accusoft’s ImageGear provides an extensive array of file conversion tools that allow developers to easily save multiple document and image file types into PDF format. With these conversion capabilities built into the back end of their applications, developers can help customers streamline their file management.
Converting Microsoft Documents to PDF
ImageGear supports the conversion of multiple Microsoft Office documents, including Word (DOCX/DOC), Excel (XLSX/XLS), and PowerPoint (PPTX/PPT). The conversion engine supports all text elements, raster images, and graphic shapes for Microsoft Office Open XML and Microsoft Office 97-2003 formats. It can convert the entire document into a PDF as well as any designated page or page ranges. The following examples show how this can be done using C#.
Converting Microsoft Word to PDF
To convert a Microsoft Word document in its entirety, the first step involves loading the ImageGear filters to create the input and output instances:
ImGearFileFormats.Filters.Add(ImGearOffice.CreateWordFormat());
ImGearFileFormats.Filters.Add(ImGearPDF.CreatePDFFormat());
For the next step, the PDF library needs to be initialized:
ImGearPDF.Initialize();The ImGearFileFormats.LoadDocument method is then used to read all pages of the file:
ImGearDocument igDocument;
using (FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(inputFileName, FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read, FileShare.Read))
{
igDocument = ImGearFileFormats.LoadDocument(fileStream);
}
Finally, the ImGearFileFormats.SaveDocument method is used to save the output PDF:
using (FileStream fileStream = new FileStream(outputFileName, FileMode.Create,
FileAccess.ReadWrite))
{
ImGearFileFormats.SaveDocument(igDocument, fileStream, 0,
ImGearSavingModes.OVERWRITE, ImGearSavingFormats.PDF, null);
}Converting Microsoft Excel and PowerPoint to PDF
The process for converting Excel and PowerPoint files follows the same basic format as converting Word files. First, initialize the input, then modify the sample code from above for the appropriate formats.
To initialize Excel:
ImGearFileFormats.Filters.Add(ImGearOffice.CreateExcelFormat());To modify sample’s open file dialog for XLSX/XLS extensions:
ofd.Filter = @"DOCX files (*.docx)|*.docx|XLSX files
(*.xlsx)|*.xlsx|XLS files (*.xls)|*.xls";To initialize PowerPoint:
ImGearFileFormats.Filters.Add(ImGearOffice.CreatePowerPointFormat());
To modify sample’s open file dialog for PPTX/PPT extensions:
ofd.Filter = @"DOCX files (*.docx)|*.docx|PPTX files
(*.pptx)|*.pptx|PPT files (*.ppt)|*.ppt";
Converting an Image File to PDF
ImageGear PDF supports the conversion of multiple image types into PDF format just as easily as it converts documents, but the process looks a bit different in code. After initializing PDF support for ImageGear.NET, the following C# example can be used to load an image file and then save it as a PDF page. The conversion process can be used for any file format that ImageGear supports.
using System;
using System.IO;
using ImageGear.Core;
using ImageGear.Formats;
using ImageGear.Formats.PDF;
using ImageGear.Evaluation;
public void SaveImageAsPDF(string inputFilePathName, string outputFilePathName)
{
try
{
const int FIRST_PAGE = 0;
// Initialize evaluation license.
ImGearEvaluationManager.Initialize();
ImGearEvaluationManager.Mode = ImGearEvaluationMode.Watermark;
// Initialize common formats.
ImageGear.Formats.ImGearCommonFormats.Initialize();
// Add support for PDF and PS files.
ImGearFileFormats.Filters.Insert(0, ImGearPDF.CreatePDFFormat());
ImGearPDF.Initialize();
// Load required page from a file.
ImGearPage page = null;
using (Stream stream = new FileStream(inputFilePathName, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read))
page = ImGearFileFormats.LoadPage(stream, FIRST_PAGE);
// Save page as PDF document to a file.
using (Stream stream = new FileStream(outputFilePathName, FileMode.Create, FileAccess.Write))
ImGearFileFormats.SavePage(page, stream, FIRST_PAGE, ImGearSavingModes.OVERWRITE, ImGearSavingFormats.PDF);
}
catch (Exception exp)
{
// Write error to Console window.
Console.WriteLine(exp.Message);
}
finally
{
// Call PDF engine terminating in any case.
ImGearPDF.Terminate();
}
}
Add Conversion Flexibility to Your Application with ImageGear
Accusoft’s ImageGear provides applications with comprehensive conversion, annotation, and viewing support for PDF files. As part of the broader ImageGear collection, it also delivers powerful image processing capabilities and support for multiple document and image file types. These features can help turn any application into a robust document management platform capable of streaming workflows and empowering collaboration.
If you’re ready to see how the SDK will function as part of your development environment, start your free trial and get straight to the code.

Accusoft’s ImageGear is a powerful image processing SDK integration that allows software developers to give their applications the ability to open, convert, and transform multiple image file formats. Given the complexity of image processing tasks, turning to a comprehensive SDK can save significant time and headaches in the software development cycle. Rather than building image manipulation features from scratch or seeking out multiple open source solutions for every processing need, developers can use ImageGear to add image processing essentials and whatever capabilities they need to keep their project on schedule.
8 Essential ImageGear Features
ImageGear delivers several noteworthy capabilities that are worth highlighting for developers looking to add image processing features to their applications. Here are a few of the most essential:
1. General Use Tools
Although ImageGear delivers a wide range of advanced image processing capabilities, it also provides a variety of conventional tools for image modification. Developers often incorporate these features into their application’s viewing interface, which allows users to easily alter images as needed. Some of the more commonly used tools include:
- Image cropping
- Image rotation and resizing
- Thumbnail creation
- Sharpening/smoothing filters
- Contrast adjustment/gamma correction
- Red eye removal
2. Region of Interest Selection
Using ImageGear’s region of interest (ROI) features, it’s possible to create a freely shaped image area that can be targeted for additional processing. The ROI can be an ellipse or polygon shape, or it can be drawn freehand. Marking a specified area creates a 1-bit mask image to indicate which pixels will be affected by image processing algorithms.
3. Erosion/Dilation
ImageGear deploys mathematical morphology operations to help clean up and enhance binary images. Erosion works by removing layers of pixels from the inner and outer boundaries of defined regions in the foreground. This causes the white pixels in the foreground to shrink, which has the effect of making the area darker. Dilation performs the opposite function, increasing the boundaries of those same pixels to make the image region lighter. These functions are typically deployed in combination to remove objects or smooth borders on black and white or grayscale images.
4. Edge Detection
A key image processing capability, edge detection is used in pattern recognition, image matching, and 3D vision applications to identify the boundaries of objects within images. This function is particularly useful for image segmentation and data extraction tasks.
5. Speckle Removal
Speckling is the distinctive “salt and pepper” noise commonly found in many scanned or low resolution images. ImageGear has two different ways of removing speckles from an image to reduce noise and improve the overall quality without blurring details.
- Despeckle Method: Removes color noise from a 1-bit image by finding the average color value within the ROI and replacing the other pixels in the speckle area with this value.
- GeomDespeckle Method: Uses the Crimmins complementary hulling algorithm, which sends the image through a geometric filter that reduces speckle noise without compromising the edges of the original image.
6. ImageClean
The ImageClean function is a multi-faceted cleanup tool that uses several classes to perform common image processing tasks. Some of those tasks include:
- Inverting white text or auto-inverting black text on a white background.
- Auto-orientation or auto-cropping of an image.
- Cleaning borders.
- Dotted or solid line removal.
- Punch hold removal.
7. Background Correction
ImageGear can identify the best-fit plane for an image and then adjust the image luminance tilt accordingly, either by increasing or decreasing the image plane. This method is particularly effective at correcting illumination gradients in low-quality digitized images.
8. Image Effects
As part of its image processing capabilities, ImageGear provides a wide array of image effects that can be used to transform or modify image files. Developers can easily integrate these tools into their application’s viewer to allow end users to easily alter images. Some of these image effects include:
- Aging Effect: This effect adjusts image saturation and contrast to make an image appear worn and old. Noise and random vertical lines are also added to enhance the effect.
- Boost Effect: Often used to make older or faded images look new and more vibrant, this effect increases saturation, brightness, and contrast.
- Drop Shadow: This method adds a drop shadow to an image, which is often useful for setting an image apart from a background when combining visual elements.
- Gaussian Blur: Typically used to smooth out composited images, this effect blurs pixels to soften images and make them appear slightly (or extremely) out of focus.
- High Density Range Effect: This effect increases the contrast of shadow, highlight, and midtone areas separately, which mimics the human eye’s ability to adjust to lighting conditions rather than applying a uniform contrast adjustment.
- Lens Flare Effect: Commonly used to make images appear more dramatic or realistic, this method simulates a bright light reflecting within the camera lens.
- Solarize Effect: This effect sets a light threshold and then inverts the colors of any pixels that exceed that value. When applied to an image, it mimics the look of photographic film that was exposed to too much light during development.
- Toy Camera Effect: Often used to liven up an image, this effect emulates the distortions and imperfections created by using a low-quality camera lens in poor shooting conditions.
- Sketch Effect: By blending the original image with a texture image, this effect can make the image look like it was sketched with a pencil or charcoal.
- Artistic Effects: This feature includes a series of effects that make images look as if they were hand painted. Two of these methods, the Pointillist and Splatter methods, use randomly generated pixel elements that cause the resulting image to be different each time the method is applied.
Expand Your Image Processing Capabilities with ImageGear
The features listed above only scratch the surface of ImageGear’s capabilities. In addition to essential image processing tools, the SDK also allows developers to add document features like annotation, conversion, compression, and full-page optical character recognition (OCR). With support for dozens of file formats, ImageGear gives software teams the tools they need to expand their application’s capabilities without wasting months of valuable development time. To get a first-hand look at what ImageGear can do for your .NET application, download a trial today.

Periods of great disruption often have a way of presenting opportunities to companies willing to make the right investments in the future. That’s been especially true of the COVID-19 pandemic, which demonstrated that many organizations are, in fact, capable of implementing rapid and sweeping technology changes when they prioritize such initiatives. A survey of executives by McKinsey found that companies implemented significant digital transformations 20 to 25 times faster than expected, largely due to urgency and the removal of longstanding roadblocks.
By undertaking major technology upgrades now, businesses can position themselves for future success before a new status quo settles in to stifle change. Companies would do well to focus their attention on a few potential areas where their applications could support digital transformation efforts with just a bit of customization.
The Great Remote Migration
The COVID-19 pandemic forced many organizations to rapidly implement the policies and technology necessary to support a remote working environment. Even though the vaccine rollout has made it possible for people to return to the physical office, not every company is rushing to bring everyone back. According to a survey of enterprise CEOs, 68 percent of large organizations are planning to downsize their office footprint and keep at least some portion of their workforce remote.
Although it no longer seems likely that remote work arrangements will completely replace traditional in-person offices, it does appear that the hybrid workforce is gaining popularity as the new normal for organizations. These workplaces will maintain a physical office presence while also incorporating a large number of remote employees. In some cases, these remote workers will be geographically distributed and never set foot in the office. This will allow companies to tap into broader talent pools from around the world. In other cases, employees will be given the option to work remotely under certain conditions, allowing them to decide when they have to actually travel to the office.
Both arrangements will present a number of challenges from a technology and a policy standpoint. In order to create a successful hybrid workplace, companies must continue to make investments in the digital document management technologies that make remote work possible. In addition to managing the myriad security challenges posed by remote employees, they also need to rethink how to handle documents now that passing paper for processing is not as simple as walking that paper document down the hall. Developers can support the transition by focusing their efforts on building robust applications that can be accessed anywhere and can handle the viewing and processing of digitized documents.
Shifting Customer Expectations
Another major change coming out of the pandemic is the extent to which customers now expect brands to offer a better digital experience with their services. Not only do people use more digital services, but their expectations about how those services should respond to their needs also underwent a significant change. They expect services to be faster and less complicated, and their tolerance for experiences that fall short of those expectations will be lower than ever in the years to come.
Organizations that fail to invest in technology and applications that allow them to better address customer demands will find themselves falling behind in an increasingly competitive landscape. That creates tremendous opportunities for developers to build and market software that does a better job of creating a seamless link between companies and their end-users. That will include user experience features like better document viewing, more accurate data capture, and improved automation tools.
Developers are also under pressure to design innovative applications that can transform business processes and help companies get an edge over their competitors. Sophisticated features powered by machine learning and big data can provide valuable business intelligence and automate low-value tasks to boost productivity. To focus on those capabilities, developers will increasingly rely on third-party SDK and API solutions to deliver core functionality like viewing, conversion, annotation, and compression. By relying on proven, ready-made solutions, they can dedicate more time and resources to innovation.
Rethinking Document Lifecycle Technology
Even before the pandemic, organizations were trying to consolidate and simplify their technology infrastructure to eliminate unnecessary sprawl and software redundancies. Often referred to as application rationalization, this trend will undoubtedly continue as companies look to maximize efficiency to reduce costs while enhancing productivity. One business process that will certainly get a closer look is document lifecycle management.
Traditionally, companies have relied upon multiple software tools to handle the operations associated with each step of the document lifecycle. Common tasks like document scanning, form identification, data extraction, file conversion, viewing, and annotation could all be performed by distinct applications, forcing employees to constantly switch between programs and copy or move files in order to work with them. This process is not only grossly inefficient but also greatly increases the risk of human error or version confusion.
Thanks to a new generation of SDK and API tools, developers can easily add new features to their software products that help to streamline and consolidate key elements of digital document lifecycles. From HTML5 viewing capabilities that make it easier to convert and open files within a web browser to more sophisticated data capture and document assembly tools that make true automation possible, these easy-to-implement integrations allow applications to carry out more essential workflow tasks without having to rely on external support.
Upgrading Your Application’s Potential with Accusoft
As organizations seize the opportunity to make essential technology upgrades, developers must be ready to provide them with the innovative applications capable of replacing legacy systems and keeping pace with customer expectations. Building software with the extensive functionality that companies require will continue to be a challenge for software teams facing budget and resource limitations. By turning to a partner with the right software integrations, they can quickly implement a wide spectrum of powerful features while keeping their own development efforts focused on designing best-in-class capabilities and bringing them to market quickly.
Accusoft’s collection of SDK and API solutions allows you to build a variety of powerful processing tools into your applications. Whether you need the conversion, viewing, and annotation features of PrizmDoc Viewer, the robust back-end processing capabilities of ImageGear, or the automated forms processing tools of the FormSuite Collection, our family of software integrations can help your application meet the varied needs of today’s companies. Learn more about our SDK and API solutions and explore how they can make your current project even more impressive.
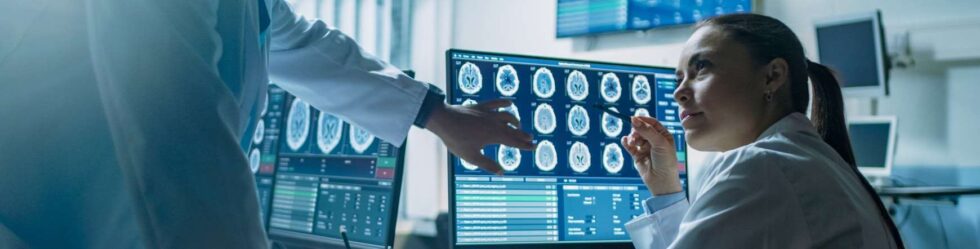
At its core, an electronic health record (EHR) system is a collection of patient-related information that is stored digitally. What began as a way for medical professionals and healthcare facilities to reduce filing cabinets filled with patient information in favor of an easier and more productive experience has evolved into one of the central tools medical providers use to manage patient care.
The State of Electronic Health Records Today
The Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act of 2009 included multiple federal incentives and regulatory guidelines to encourage healthcare providers to adopt EHR systems. At the time, only 12.2 percent of acute care hospitals had access to even rudimentary EHR software. Just over five years later, more than 80 percent of them had an EHR system in place. By 2017, 96 percent of all hospitals would be using them, along with 86 percent of physician offices.
Today, EHR applications are the key to sharing information across healthcare networks. When deployed and managed effectively, they give medical professionals the ability to provide a deeper level of care thanks to the information they make readily available and the ease of sharing that information with every provider involved in a patient’s care. A physician can quickly review a diagnosis, determine what tests have been performed, and track prescription histories simply by opening a patient’s file, which can eliminate confusion and redundancies. More importantly, patients can access their own medical records to stay up to date on their treatment plans and make informed decisions about their own care.
5 Ways EHR Systems Will Change Over the Next 5-10 Years
Despite their widespread adoption, however, EHR systems are still evolving. No one is more aware of that fact than the healthcare professionals using them. According to a 2018 Stanford study, 59 percent of primary care physicians believed that their EHR software was in need of a significant overhaul. Part of the challenge is that many of today’s EHR systems are based on antiquated electronic medical records (EMR) systems that were confined to a single practice and not meant to accommodate complex, overlapping workflows between different providers.
Over the next five to ten years, a new generation of EHR applications will continue to revolutionize the healthcare industry and hopefully provide even better patient outcomes.
1. Improved Interoperability
In an ideal world, every EHR system would communicate with other systems seamlessly, allowing records to be accessed easily from anywhere at any time. Unfortunately, that’s not always the case. Medical records come in a variety of forms and formats, and not every provider has the software in place to access and view them. In a 2020 survey of US physicians, Deloitte found that 84 percent of them believe that sharing data in a “secure, streamlined, and timely” fashion will be one of the biggest priorities of EHR systems over the next decade.
2. Security and Privacy Improvements
Considering the large amount of private information contained in EHR systems, it’s no surprise that security is always a major concern. While the healthcare industry has suffered a number of high profile (and expensive) data breaches over the last decade, it’s also a sector that’s uniquely vulnerable to insider threat. In fact, according to a 2018 Verizon data breach report, the healthcare industry is the only industry where insider threats actually outnumber external threats, such as cyberattacks. In the coming years, EHR developers will need to consider new strategies for preventing the inappropriate access of sensitive healthcare data.
3. Telehealth Integration
The COVID-19 pandemic sparked a long-overdue revolution in telehealth, with many insurance providers and hospitals now offering, or even encouraging, remote interactions between patients and physicians. With telehealth integration, patients and their healthcare professionals can be linked remotely, breaking down the natural barrier of geography at the same time. A doctor can provide care to a patient in a remote rural area, for example, essentially paving the way for a remote consultation to occur within the electronic health record system itself. While the technology already exists for a doctor to examine a patient over video conference, EHR integration will make it easier to collect and document information related to remote consultations.
4. Rethinking Usability
For all the advantages of EHR systems, their current incarnation imposes tremendous administrative burdens on healthcare professionals. A study from 2017 revealed that the average clinician spends about six hours of their day interacting with EHR software, which could explain why burnout and stress are so common in the healthcare field. Part of the problem is that many early EHR systems weren’t designed with significant input from the people who actually had to use them. By working closely with medical professionals, EHR developers can better adapt their applications to fit the needs of today’s providers. They can also deploy automation tools to eliminate cumbersome manual processes that contribute to burnout and are prone to human error.
5. Better Patient Access
One of the promised benefits of EHR systems was that they would allow patients to access their medical records to better manage their healthcare decisions. Unfortunately, this promise has yet to materialize. A 2019 study found that just 10 percent of patients with online access to their records have actually accessed them. Part of this is no doubt due to a lack of proper guidance and awareness, as 63 percent of patients who do view their records were first encouraged to do so by their provider. In anticipation of potential regulatory changes that require providers to promote more frequent patient access, developers can take the lead by building EHR software that is easier for patients to use on their own. Web applications with HTML5 viewing capabilities will allow patients to view their medical records without having to download any files or software, which will also make it easier for providers to communicate and share information with them.
Choosing the Right Integrations for EHR Systems
As EHR developers look to incorporate new features and tools into their applications, they’re going to need the right SDK and API integrations to keep development schedules on track and manage their resources effectively. Accusoft’s collection of document and image processing integrations allow developers to quickly implement powerful viewing, conversion, compression, and automation features so they can continue to focus on crafting a better EHR experience. From PrizmDoc Viewer’s versatile HTML5 viewing capabilities to ImageGear Medical’s ability to manage complex DICOM files, our software solutions are already helping EHR systems evolve to meet the changing needs of physicians and patients.
Find out how the right integrations can help your EHR application take advantage of opportunities in the years to come. Download the first volume in our EHR eGuide series to learn more today.

Printers, scanners, and other imaging devices have long been a source of headaches and frustration for developers and users alike. All too often, multiple software tools are required to connect an application to a device and acquire image files from them. This not only slows down workflows, but also creates opportunities for human error. Files can easily be misplaced or imported using the wrong parameters under these conditions.
Thanks to ImageGear’s TWAIN scanning support, however, developers can ensure that their application makes acquiring images from compatible devices both straightforward and mistake free.
What Is TWAIN?
Developed in 1992 by a consortium of software developers and hardware manufacturers, the TWAIN standard is a standard software protocol and API that facilitates communication between imaging devices and software applications running on a computer. The word itself refers to a famous line in the Rudyard Kipling poem “The Ballad of East and West” that reads “never the twain shall meet.” Although sometimes alleged to stand for “Technology Without An Interesting Name,” the term is not actually an acronym despite being capitalized.
The name is well chosen because the TWAIN standard helped to solve the enduring problem of getting imaging devices and computers to connect and send data between one another. Most commonly used for scanners and digital cameras, TWAIN made it possible to request an image file to be imported into an application without having to utilize additional software or input commands using the physical device.
Implementing TWAIN Scanning with ImageGear
As a versatile image processing SDK, ImageGear fully supports the TWAIN specification, which allows developers to support any TWAIN-capable device directly into their applications. In most instances, this will involve adding a “Scan” button or option somewhere in the platform’s interface so that users can quickly and easily instruct their scanner to capture an image and pass it along to the application’s storage or workflow. Developers can also use the integration to adjust device settings directly from their application, such as changing the scanning area, modifying brightness and contrast, or increasing/decreasing dots-per-inch (resolution).
ImageGear’s TWAIN scanning feature works with three external elements to facilitate image file transfers:
- The Device: Usually a scanner or digital camera, this is the primary imaging source. The device must be compliant with TWAIN protocol.This is typically indicated by the manufacturer.
- Data Source: Although ImageGear’s TWAIN scanning features can connect an application to a scanner, the device still needs a software driver that allows it to communicate with the computer’s operating system.
- Data Source Manager: The TWAIN manager software provides a universal mechanism for managing and using data sources from different device manufacturers. Developed by the TWAIN consortium, it can be downloaded for free and installed wherever the application is running.
(Both the device’s data source driver and TWAIN data source manager should be included with its installation software. They are not provided by the ImageGear SDK).
Acquiring an Image Using TWAIN Scanning
ImageGear can configure an application to gather an image or set of images from a connected device with a few simple steps.
Step 1: Open the Data Source
Developers can set the application to automatically open a default Data Source. This is typically the best choice when only one scanner is available, as is often the case in a small workplace. They can also use the Data Source Manager to provide a list of all available Data Sources and let the user select the one they need.
Step 2: Adjust Settings
ImageGear’s TWAIN scanning features allow image acquisition parameters to be set through the application. Parameters such as page count and image size can be set to a common default, but developers can also give the option to obtain the various capabilities (listed as “ScanCaps”) and display them for users to select from. ImageGear supports a wide range of TWAIN-related capabilities.
Step 3: Acquire Image
After all settings are configured, the image can be scanned and loaded into an ImGearPage Class object. When acquiring a multi-page image, ImGearPages are loaded into an ImGearDocument Class object instead.
How ImageGear TWAIN Scanning Looks in Code
As an example, here’s what the C# code may look like when using ImageGear to help an application import an image from a TWAIN Data Source:
using System;
using ImageGear.Core;
using ImageGear.TWAIN;
public ImGearPage AcquireImage(IntPtr Handle)
{
ImGearPage igPage = null;
ImGearTWAIN igTWAIN = new ImGearTWAIN();
igTWAIN.WindowHandle = Handle;
igTWAIN.UseUI = true;
try
{
// Open the data source selection dialog
igTWAIN.OpenSource(String.Empty);
// Initialize the scanning
igPage = igTWAIN.AcquireToPage();
}
catch(ImGearException e)
{
// Handle the exception ...
}
finally
{
if(igTWAIN.DataSourceManagerOpen == true)
{
igTWAIN.CloseSource();
}
}
return igPage;
}
Expand Your Application’s TWAIN Support with ImageGear
Accusoft’s ImageGear SDK provides comprehensive support for a broad range of TWAIN devices, which makes it easier than ever for developers to control the scanning process directly from their applications. Integrating TWAIN scanning can streamline workflows and significantly improve the software user experience by completely eliminating the need to turn to external programs for image acquisition. ImageGear is fully compatible with multiple generations of the TWAIN standard, including TWAIN v1.6, v1.7, v1.8, v1.9, and v2.4.
In addition to TWAIN scanning support, ImageGear provides powerful image and document processing capabilities that can transform your application workflows. With extensive file conversion and compression features, it’s the best way to quickly integrate content management features into your platform. To get a glimpse of what ImageGear can do for your .NET application, download a free trial today and start building.

Although digital solutions are gradually finding their way into legal practices, there is still a great deal of progress that needs to be made with regards to the discovery process. The dramatic growth of electronic documents over the last few decades has seen the emergence of eDiscovery, which involves all electronic aspects of gathering, identifying, and producing information in preparation for a lawsuit or investigation. Resources gathered during the eDiscovery process are referred to as electronically stored information (ESI) and can consist of things like documents, emails, databases, voicemails, audio/video files, website content, and social media posts.
Today’s LegalTech developers have created a variety of applications to streamline the eDiscovery process and make it easier for legal teams to comply with the regulations pertaining to the management of ESI. Unfortunately, 48 percent of legal professionals admit that their organization is still conducting much of their research and discovery manually.
By continuing to rely on cumbersome, error prone manual processes, these organizations are missing out on many of the benefits offered by eDiscovery software. This creates an opportunity for LegalTech developers that are continuing to build eDiscovery tools to meet the evolving needs of the legal industry.
5 Undiscovered Benefits of eDiscovery Tools
1. Lower Costs
While there’s a lot more to eDiscovery software than cost savings, it’s important for firms and departments to understand just how much time they could be saving with eDiscovery tools. According to data from Thomson Reuters, the typical lawyer takes about 51 minutes to locate a key document during the litigation process, but using an eDiscovery solution can reduce that time to a mere 16 minutes. The saved time can easily be directed toward more high value tasks, which allows firms to deliver better value to their clients.
LegalTech developers can help deliver these cost-effective platforms by keeping their own costs under control. Implementing key features like file viewing and document assembly by way of SDKs and APIs rather than building them from scratch is one of the best ways to keep projects on time and under budget.
Designing user interfaces that legal teams can quickly understand and use effectively is also crucial because it increases the likelihood that new platforms will be adopted and used within a firm. Any discovery tasks that can be automated should be integrated into application workflows so that lawyers can spend less time managing documents and more time honing their legal strategy for a case.
2. Better Information
One of the challenges of discovery is the sheer quantity of information that needs to be managed. While a small case may only amount to a gigabyte or two worth of documents, that data could very easily consist of hundreds of files, many of which might not have any relevance to the case itself.
This is especially true when it comes to records of electronic communication. Simply CCing a relevant party on an email, for instance, could suddenly add dozens or even hundreds of emails to the discovery process. The right eDiscovery tool can help to winnow down this massive trove of data by screening documents for relevance and eliminating redundant or immaterial information.
LegalTech developers can streamline the eDiscovery process by incorporating powerful full-text search tools that can help litigators find what they need quickly and easily. Documents can even be assigned barcodes as they’re scanned into the system so they can be routed to the proper storage location while their metadata is passed along to a database for easy reference in the future. Comparison tools can help identify differences between similar documents and avoid redundancies.
3. Privacy Protection
Although most legal teams understand the importance of protecting confidential and private information found in so many documents, they don’t always know the best way to protect it. Redacting content from printed documents can be difficult enough, but all kinds of mistakes are frequently made when it comes to digital files.
Without dedicated eDiscovery software, firms and departments often end up making classic redaction mistakes like covering text with a black box or changing the text color to match the document background. Using the right eDiscovery tools to redact sensitive content helps to ensure that firms are complying with relevant privacy laws.
When it comes to incorporating redaction features into their eDiscovery software, LegalTech developers need to think beyond the purely visual aspects of redaction. True redaction requires more than simply burning annotation markups into a document.
Any redaction tools they provide must be able to actually remove sensitive content from a file while still retaining an original, unaltered original for internal use and ESI compliance purposes. They should also give users the ability to add redaction reasons when content is removed to provide better context and justification for why it was excised from the document.
4. Compliant ESI Retention
There are complex standards in place governing the preservation of ESI to ensure that the integrity of documents is maintained. Failing to comply with those laws can result in substantial fines and penalties.
While the digitization of documents should make preserving them much easier than the hard work of maintaining physical files, the task can quickly become chaotic without a dedicated eDiscovery solution. Manually saving files to hard drives without any clear structure is a recipe for files being misplaced. Even worse, improperly converting files from one format to another could alter or erase metadata that is vital for demonstrating ESI compliance.
By building versatile document management and conversion tools into their eDiscovery tools, LegalTech developers can ensure that files are being preserved in accordance with ESI standards. Centralizing all eDiscovery content into a singular workflow makes it much easier to locate any version of a file at any time.
Once the review process is completed, it’s not uncommon for attorneys to combine many important documents into a single file for easy reference or to break a long document up into several smaller sections. Effective conversion tools should leave the original version of the file intact, along with any unredacted and unannotated versions of documents.
5. Improved Access to Data
Courtrooms and legal organizations may still rely on paper for many processes, but during the discovery process, they need to be able to manage a dizzying array of file formats as they gather documents, images, and other sources of information. Some legal teams think they will be able to “get by” relying on a patchwork of software to access this data.
Unfortunately, managing eDiscovery documents with conventional word processors, PDF readers, and email applications is a recipe for confusion and frustration. Files can be lost or altered easily, and sharing them over email can create significant security risks. Dedicated eDiscovery software provides a central hub that not only makes it easy to access and view information, but also allows legal teams to control who has permission to open or comment on files in the first place.
Developers can easily turn their LegalTech solution into a powerful, collaborative eDiscovery platform by incorporating HTML5 viewing technology. With its ability to display multiple different file formats, an HTML5 viewer allows legal teams to open and review documents, images, and other file types gathered during the discovery process without having to switch between multiple applications.
For LegalTech developers, integrating an HTML5 viewer is a simple way to quickly give users the ability to access the information they need. Since the viewer can run in a web browser, there’s no need to build a complex viewing solution from the ground up, which could pull resources away from working on other innovative LegalTech tools.
Enhance Your eDiscovery Capabilities with Accusoft
Accusoft’s collection of SDKs and APIs provide LegalTech developers with a broad range of tools that allow them to add powerful features to their applications. Whether it’s the broad HTML5 viewing, annotation, and redaction capabilities of PrizmDoc Viewer or the data capture and conversion tools offered by ImageGear, our integrations deliver the functionality to support your innovative eDiscovery tools.
Check out our whitepaper to find out how implementing the right features can help your LegalTech application capitalize on the latest trends in the eDiscovery software and services market. Talk to one of our LegalTech solutions experts today to learn how Accusoft integrations can unlock your solution’s full potential.

The world of investment technology moves almost as quickly as the investment markets themselves. Without the right FinTech tools, today’s individual investors are likely to be left behind the latest financial trends. That’s why FinTech investment solutions are once again becoming a major point of emphasis for developers looking to expand access to key financial services.
The History and Impact of FinTech Investment Solutions
As a subset of the FinTech industry, “invest-tech” is sometimes used to refer to a wave of innovative investment management technologies that are helping to connect aspiring investors to the information and financial services they need to capitalize on new opportunities. Like many other FinTech applications, investment software tools have played a pivotal role in expanding access to financial markets and helping consumers take direct control of their investment decisions.
Much of the early FinTech investment market was driven by “robo-advisor” services that used sophisticated algorithms to provide customers with investment guidance. The boom reached its peak in the mid-2010s, with a record 81 new invest-tech solutions hitting the market in 2014. Since then, the number of launches has dwindled as established incumbents in the financial services sector moved in to acquire some of the most promising firms.
In many instances, those acquisitions were made to expand existing digital capabilities or to secure a new base of established investment customers. Since the typical FinTech investment user was younger and possessed fewer assets, the profit margins for many start-ups were simply too low and the costs of customer acquisition too high. This dynamic has gradually shifted the industry’s focus toward the B2B market, although crowdsourced investment platforms remain quite popular among many retail investors.
The Current State of FinTech Investment Technology
FinTech investment platforms roared back into the public consciousness following the COVID-19 pandemic as the combination of work-from-home mandates and accumulated savings caused a rise in retail investment. Individual investors made up 19.5 percent of stock market activity in the first half of 2020, an increase of nearly five percent from the previous year. On a particularly busy day of trading, individual investors constitute a whopping 25 percent of market activity.
Thanks to mobile FinTech apps from startups and established players in the financial services industry, more people than ever before have access to investment opportunities, which has caused significant disruption to the market. The controversial rush on GameStop stock in early 2021, for instance, demonstrated just how much impact easy-to-access these platforms could have on investment trends.
This resurgence in retail investment could very well spark another wave of interest in FinTech investment apps, especially from established firms looking to expand their digital capabilities and capitalize on the growing market.
Enhancing the FinTech Investment Experience
For developers building the latest iterations of FinTech applications, there are a few key features worth focusing on to deliver a better investment experience.
Sharing Data and Portfolios
While being able to access investment portfolio data on demand is valuable, customers are understandably concerned about the security of that data. Whether they’re building a retail investment app or a managed digital vault, developers need to provide a way of viewing private information securely. This is especially critical for digital documents. Relying on an external application for viewing or even just using the default browser viewer could potentially expose information to unauthorized users. By integrating secure, native viewing features, developers can ensure that investment portfolio data remains within a protected application environment.
Protecting Proprietary Research
One of the key benefits of working with an investment firm is having access to their market research when making financial decisions. In many cases, financial projections are calculated using proprietary formulas embedded within spreadsheets. Unfortunately, spreadsheets pose a number of security and compatibility problems. Even if a workbook is shared securely, there’s often little to stop someone from copying the proprietary formulas embedded within the cells and using it for other purposes. FinTech developers need ways to make those spreadsheets available without also compromising the valuable formulas developed over years of painstaking research.
Improving Data Capture
Making the right investment is all about having the right information. That data could come from a variety of sources, and in many instances it will need to be collected and analyzed before it can be of any use. Automating the data capture process can help to get that information into a customer’s hands faster. For example, customer information can be updated quickly by automatically extracting data from structured forms like tax filings. Scanned documents can also be converted into searchable PDFs using Optical Character Recognition (OCR), which makes it easier for AI-powered tools to sift through data in search of trends and potential opportunities.
Choosing the Right FinTech Investment Integrations
Building a successful FinTech application requires developers to build innovative tools that set them apart from the competition while also implementing everyday functionality that often lies outside their experience or expertise. Features like document viewing, annotation, and file conversion may be integral components of their platform, but take both time and development resources to build from scratch. By turning to SDKs and APIs, developers can quickly roll out new features without detracting from their primary software development goals.
Accusoft has been working with FinTech investment platforms for many years, helping developers to build powerful InsureTech applications without sacrificing the viewing and image processing technology that customers expect.
- PrizmDoc Viewer: Adds secure HTML5 viewing, annotation, conversion, and redaction capabilities to web-based applications, allowing developers to control every aspect of the viewing experience without compromising privacy.
- PrizmDoc Cells: Provides full XLSX support for applications, making it possible to securely upload and share Excel workbooks without exposing the source file or allowing users to access and copy proprietary formulas.
- FormSuite: A versatile forms SDK that allows developers to add form template identification and data extraction to their application, making it easier than ever to automate and streamline workflows.
- ImageGear: In addition to conversion and compression tools, it also provides full-page OCR for converting scanned documents into searchable text.
Learn more about how Accusoft is helping FinTech developers to drive the next generation of investment technology platforms.
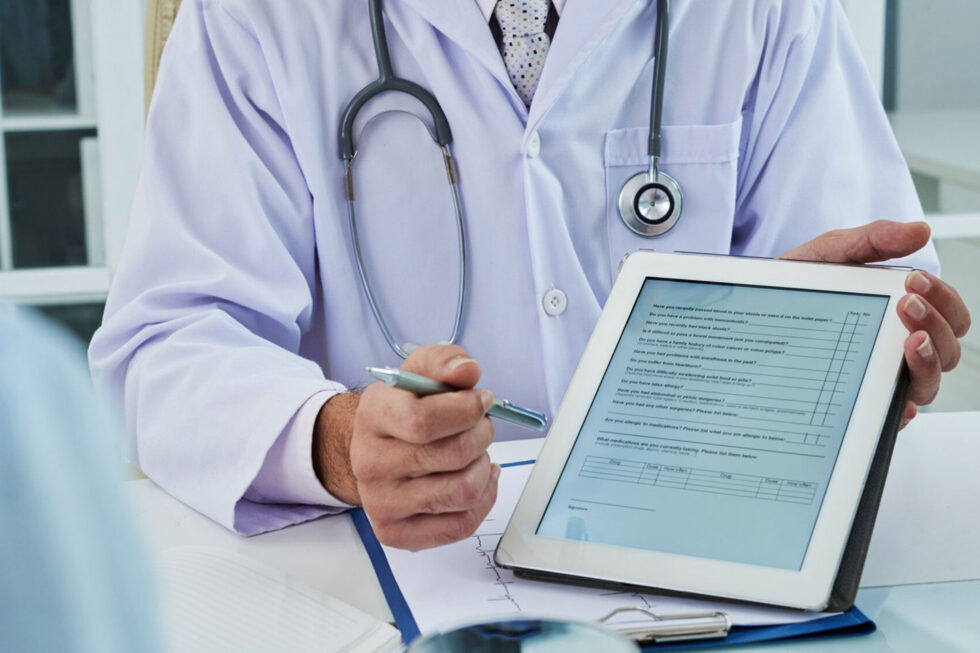

For today’s healthcare organizations, having a versatile electronic health records (EHR) system is essential for running an efficient practice and connecting to other medical providers. Thanks to EHRs, practices can ensure that they’re getting a complete picture of a patient’s health and treatment history, which allows them to deliver much better care outcomes. As developers continue to refine the usability of these systems, they need to consider how they can improve core features like healthcare electronic document management and medical imaging support.
Managing Medical Documents
A typical EHR system has to be able to handle quite a lot of document types. Anyone who has visited a healthcare provider is quite familiar with the myriad forms used to gather patient information. Many of those forms end up being converted into digital formats that need to be managed within the EHR system. Then there are digital versions of lab reports, physician notes, invoices, and financial documents.
While EHR systems may utilize databases to store much of the information they need, healthcare providers still need to be able to produce physical documents and view digital files in many situations. This could include communicating information to patients, complying with regulatory requests, or filing a financial claim of some kind. More importantly, they also rely on digital documents to enter data into the EHR system. The push toward interoperability between EHR systems has improved information sharing, but there are still many instances where medical records are delivered in the form of a document that needs to be managed securely.
Document Conversion
If an EHR application lacks the right file conversion capabilities, viewing and extracting data from those documents could prove difficult. The last thing a practice wants to do is actually remove them from the secure EHR system to open and convert the files using separate software that may not be compliant when it comes to handling healthcare information. Even if the external application is secure, transferring files over, converting them, and then transferring them back is both inefficient and creates unnecessary risk (especially if someone forgets to delete the original file or move it back into the EHR environment).
ImageGear Medical has a document conversion feature that supports a wide range of file types, allowing developers to build EHR applications capable of quickly converting incoming documents. They can even set up their solution to perform conversion tasks programmatically to help streamline workflows and minimize human error. This helps practices to get a better handle on document management, ensuring that they will be able to do everything they need with files completely within the EHR application.
Other Essential Document Features
But ImageGear Medical’s document capabilities go far beyond just conversion. With full annotation support, developers can provide markup tools within the EHR system that allow physicians to make notes and comments on various documents. This allows them to share information much more easily. If a physician has a question about a diagnosis or a prescription, for instance, they can simply leave an annotation note directly on the document rather than referring to it in a separate message.
ImageGear Medical also allows applications to perform full-page optical character recognition (OCR), which can quickly read and extract text from document and image files. This feature is especially useful for capturing text from scanned images of documents, which can then be used to create a searchable PDF or fill form fields within the EHR system. The OCR engine not only reads most Western languages, but also detects and reads several Eastern language characters.
Managing DICOM Files
One of the biggest challenges healthcare organizations face is with managing medical imaging files. When providers need to send X-Rays, MRIs, or CT Scans, they use a standardized file format known as Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) files. These files are more than just image files, however. They contain extensive datasets that provide a patient’s information along with image pixel data for multi-dimensional medical scans. A DICOM file can be quite large due to the high-resolution image data used by most medical imaging equipment.
Although most EHR systems are capable of transmitting DICOM files (via a DICOM out or DICOM send feature), they usually can’t actually view them in their native format. Since Windows doesn’t recognize them as image files, additional viewing software is typically needed to open and view them. This is why physical storage, like discs and flash drives, are often used to transfer DICOM files along with the necessary viewing software.
ImageGear Medical helps to solve the DICOM dilemma thanks to its extensive conversion and compression capabilities. By decoding the complex data contained within the file, ImageGear Medical can convert DICOM files into image formats that are much easier to view and manage. This is especially useful for smaller practices that don’t have a picture archiving and communication system (PACS) capable of storing, retrieving, distributing, and viewing high-quality medical images.
Converting DICOM files makes it possible for healthcare professionals to view them on any device connected with their EHR system. That could include tablets or other IoT devices that healthcare technology companies are rolling out to put critical medical data on the front lines of everyday care. Developers can also use ImageGear Medical’s conversion tools to allow their EHR system to share viewable versions of diagnostic scans with patients, allowing practices to make good on the promise of providing patients access to their essential health data at all times.
The sheer size of DICOM files makes them difficult for many practices to manage. Simply compressing them tends to degrade the image data, which can create significant problems when files are unpacked and opened for viewing. Losing even a small degree of image quality can make it much harder to render an accurate diagnosis. In some cases, poorly designed compression can even make it nearly impossible to uncompress again at all. Thanks to powerful lossless compression technology, ImageGear Medical makes it easier to share medical images between providers without damaging the integrity of the original data.
Expand EHR Capabilities with ImageGear Medical
Accusoft’s imaging, conversion, and compression technology has been supporting the needs of the healthcare industry for decades. As developers work to expand the capabilities of their EHR applications, our engineers are busy improving the medical SDKs that will provide them with the features they need to stand out in a competitive market.
ImageGear Medical utilizes a combination of efficient code and elegant APIs to deliver the document and image processing tools EHR systems require. For a closer look at this dynamic SDKs capabilities, check out our extensive developer resources today or download a free trial to get started.
The industry-wide push to digitize documents and minimize the use of physical paperwork has made PDF one of the most ubiquitous file formats in use today. Business and government organizations use PDFs for a variety of document needs because they can be viewed by so many different applications. When it comes to archiving information, however, PDFs have a few limitations that make them unsuitable for long-term storage. That’s why many organizations require such files to be converted into the more specialized PDF/A format. Learn how easy it is to convert PDF to PDF/A with ImageGear.
What Is PDF/A?
Originally developed for archival purposes, the PDF/A format is utilized for long-term preservation that ensures future readability. It has become the standard format for the archiving of digital documents and files under the ISO 19005-1:2005 specification. Government organizations are increasingly utilizing PDF/A to digitize existing archival material as well as new documents.
The distinctive feature of PDF/A format is its universality. Although PDFs are well entrenched as the de facto standard for digital documents, there are many different ways of assembling a PDF. This results in different viewing experiences and sometimes makes it impossible for certain PDF readers to even open or render a file. Because PDF/A documents need to be accessible in the indeterminate future, there are strict requirements in place to ensure that they will always be readable.
PDF vs PDF/A
While PDF and PDF/A are based upon the same underlying framework, the key difference has to do with the information used to render the document. A standard PDF has many different elements that make up its intended visual appearance. This includes text, images, and other embedded elements. Depending upon the application and method used to create the file, the information needed to render those elements may be more or less accessible for a viewing application.
When a PDF viewer cannot access the necessary data to render elements correctly, the document may not display correctly. Common problems include switched fonts (because the original font information isn’t available), missing images, and misplaced layers.
A PDF/A file is designed to avoid this problem by including everything necessary to display the document accurately. Fonts and images are embedded into the file so that they will be available to any viewer on any device. In effect, a PDF/A doesn’t rely on any external dependencies and leaves nothing to chance when it comes to rendering. The document will look exactly the same no matter what computer or viewing application is used to open it. This level of accuracy and authenticity are important when it comes to archival storage, which is why more organizations are turning to PDF/A when it comes to long-term file preservation.
How to Convert PDF to PDF/A
ImageGear supports a broad range of PDF functionality, which includes converting PDF format to a compliant PDF/A format. It can also evaluate the contents of a PDF file to verify whether or not it was created in compliance with the established standards for PDF/A format. This is an important feature because it will impact what method is used to ultimately convert a PDF file into a PDF/A file.
Verifying PDF/A Compliance
By analyzing the PDF preflight profile, ImageGear can detect elements of the file to produce a verifier report. The report is generated using the ImGearPDFPreflight.VerifyCompliance method.
It’s important to remember that this feature does NOT change the PDF document itself. The report also will not verify annotations that have not been applied to the final document itself. Once the report is generated, a status code will be provided for each incompliant element flagged during the analysis.
These codes can have two values:
- Fixable: Indicates an incompliance that can be fixed automatically during the PDF/A conversion process.
- Unfixable: Indicates a more substantial incompliance that will need to be addressed manually before the document is converted into PDF/A.
Converting PDF to PDF/A
After running the verification, it’s time to actually convert the PDF to PDF/A. The ImGearPDFPreflight.Convert method will automatically perform the conversion provided there are no unfixable incompliances. This process will change the PDF document into a PDF/A file and automatically address any incompliances flagged as “Fixable” during the verification process.
While it is not necessary to verify a PDF before attempting conversion, doing so is highly recommended. Otherwise, the document will fail to convert and return an INCOMPLIANT_DOCUMENT code. The output report’s Records property will provide a detailed report of incompliant elements. Since any “Fixable” incompliances would have been addressed during conversion, the document’s remaining issues will need to be handled manually.
This method is best used when manual changes need to be made to the PDF file prior to conversion. One of the most common changes, for example, is making the PDF searchable. Once the alterations are complete, the new file can be saved using the ImGearPDFDocument.Save method.
Other ImageGear PDF to PDF/A Conversion Methods
Raster to PDF/A
ImageGear can save any PDF file produced directly by a raster file as a PDF/A during the initial conversion. A series of automatic fixes are performed during this process to ensure compliance.
- Uncalibrated color spaces are replaced with either a RGB or CMYK color profile. This could change the file size.
- Any LZW and JPEG2000 streams are recompressed since PDF/A standards prohibit LZW and JPEG 2000 compression.
- All document header and metadata values are automatically filled in to comply with PDF/A requirements.
Quick PDF to PDF/A Conversion
For quick conversions in workflows that don’t require displaying or working with a file in any way, the ImGearFileFormats.SaveDocument method is another useful option. This process loads the original file, converts it, and saves the new version all at once. It’s important to set the PreflightOptions property to be set in the save options. Otherwise, the new document will not save as a PDF/A compliant file.
Take Control of PDF/A Conversion with ImageGear
Accusoft’s versatile ImageGear SDK provides enterprise-grade document and image processing functions for .NET applications. With support for multiple file formats, ImageGear allows developers to easily convert, compress, and optimize documents for easier viewing and storage.
ImageGear takes your application’s PDF capabilities to a whole new level, delivering annotation, compliant PDF to PDF/A conversion, and other manipulation tools to meet your workflow needs. Learn more about how ImageGear can save you time and resources on development by accessing our detailed developer resources.

Few industries have been impacted by the proliferation of digital technology than the financial services sector. In fact, it’s one of the few markets where the average consumer can easily observe how much has changed in a short amount of time. Many people haven’t even set foot inside a bank for years, and millions pay all of their bills exclusively online. According to the US Federal Reserve, personal checks declined from 58.8 percent of non-cash payments in 2000 to just 8.3 percent in 2018. Both of these trends are driven by the increased convenience of FinTech applications, and the same changes have impacted the lending industry, as well.
What Is FinTech Lending?
Since the 2008 financial crisis, a new breed of lenders has become a disruptive force in the banking sector. Unburdened by the cumbersome infrastructure that makes large financial institutions slow to adapt to change, FinTech lenders utilize the latest technology to deliver a more responsive, personalized, and transparent lending experience to consumers. These innovative startups have combined easy-to-access digital platforms with sophisticated data analytics to streamline the lending process and deliver funds to borrowers much faster than could be accomplished with traditional loans.
Borrowers, it seems, have been quick to embrace this alternative source of lending. From 2013 to 2018, FinTech companies increased their share of the personal loan market from a mere five percent to thirty-eight percent. That rapid growth is a result of increased penetration into the digital marketplace and more flexible credit scoring that allows FinTech lenders to assess risk and approve loans more effectively.
In the early days of the industry, most FinTech lenders still relied upon traditional FICO credit scores when evaluating a borrower’s potential to repay loans. Over time, however, they have used a variety of alternative scoring mechanisms driven by data collection algorithms to create a more dynamic picture of a borrower’s credit status. Between 2007 and 2015, for instance, the correlation between FICO scores and the rating system used by one prominent peer-to-peer FinTech lender declined from 80 percent to just 35 percent.
The “Tech” Behind FinTech Lending
The loan adjustment algorithms working under the hood of FinTech lending applications are incredibly sophisticated, but they need good data for fast, accurate underwriting. While traditional lenders focus on predictable data points like income, debt payments, and assets, the digital nature of FinTech applications allows them to go much more granular. By gathering insights from other customer applications, internet searches, and even geolocation data, they can create a more complex profile of each customer, which then allows them to structure loans and other financial products that meet their specific needs while also protecting the lender to unnecessary risk.
This new approach to lending has helped FinTech applications to cut down the “time to yes” on credit decisions from the three to five weeks commonly seen from traditional banks to as little as five minutes. Even more critically, they can use digital funding to deliver cash to borrowers in less than 24 hours compared to the typical lender’s three month response time.
Improving “Time to Yes” on Credit Decisions
In addition to deploying more sophisticated risk adjustment algorithms to assess credit worthiness, there are some additional ways that FinTech lenders can continue to improve performance and efficiency.
Embrace Paperless Automation
The first and most obvious step they can take is by eliminating paper forms from the application process whenever possible. One of the reasons why banks and other financial services organizations move so slowly is due to the time it takes to fill out, fax, scan, and review physical documents. Not only are these forms inefficient, but they’re also prone to clerical errors when an applicant’s data needs to be transferred from the form into a database or application. By digitizing the application process wherever possible and automating data capture, FinTech lenders can significantly cut down on processing times and eliminate the human errors that so often create additional delays.
Increase Document Management Versatility
Shifting to an emphasis on digital documentation brings another complication along with it because there are a variety of file formats used throughout the financial industry. Some documents need to be in a specific format for compliance purposes, and if customers are submitting files through a FinTech lending platform, they could be using multiple different file types.
In order to streamline processing, FinTech applications need to be able to easily convert a wide range of file types into a few key formats that work best with their processing workflows. That means FinTech developers will need to integrate powerful document conversion tools into their software to ensure that they can avoid any troublesome incompatibility issues during loan processing.
Enhance Data Capture Capabilities
Although FinTech lenders are developing incredible algorithms capable of analyzing massive amounts of data to shorten credit application times, they are still dependent upon the information made available to them. That means developers need to implement data capture tools that can pull key data from a variety of sources and compile it into an easily searchable format.
Optical character recognition (OCR) engines can quickly extract information for any number of documents and images to create searchable files that FinTech software can quickly process as needed. For hand-printed documents scanned into digital format, intelligent character recognition (ICR) tools can be deployed just as effectively, allowing FinTech lenders to gather data from a wide variety of sources.
Expand FinTech Lending Capabilities with APIs and SDKs
One of the easiest ways for FinTech developers to quickly build lending-friendly features into their applications is to leverage API and SDK integrations. Rather than building new functionality from scratch, they can instead take advantage of existing, proven solutions to enhance their applications. This allows them to keep the focus on the core differentiators of their FinTech lending platform, allowing them to process and approve loans faster while minimizing potential risk.
Accusoft’s collection of API and SDK integrations provide powerful viewing and processing capabilities when it comes to FinTech workflows. Whether you need to convert multiple file types quickly, clean up document images, or perform OCR data capture, Accusoft has the solution to unlocking your FinTech lending application’s potential.
